Ever wondered why uncommon sun spider species choose to embrace the cover of darkness for their activities, shunning the vibrant daylight?
The nocturnal behavior of these elusive arachnids unveils a realm of mysteries waiting to be unraveled.
As you ponder the secrets hidden within their nighttime movements, a deeper understanding of their survival strategies and evolutionary adaptations begins to emerge.
What nocturnal revelations lie in store for those who seek to shed light on the enigmatic world of these sun spider species?
Key Takeaways
- Sun spiders exhibit nocturnal behavior in arid habitats to avoid daytime heat.
- Nocturnal activity aids in evading predators, conserving energy, and efficient hunting.
- Unique mating rituals ensure reproductive success and genetic diversity.
- Sun spiders play a crucial role in controlling pest populations and maintaining ecosystem balance.
Habitat Preferences and Environmental Adaptation
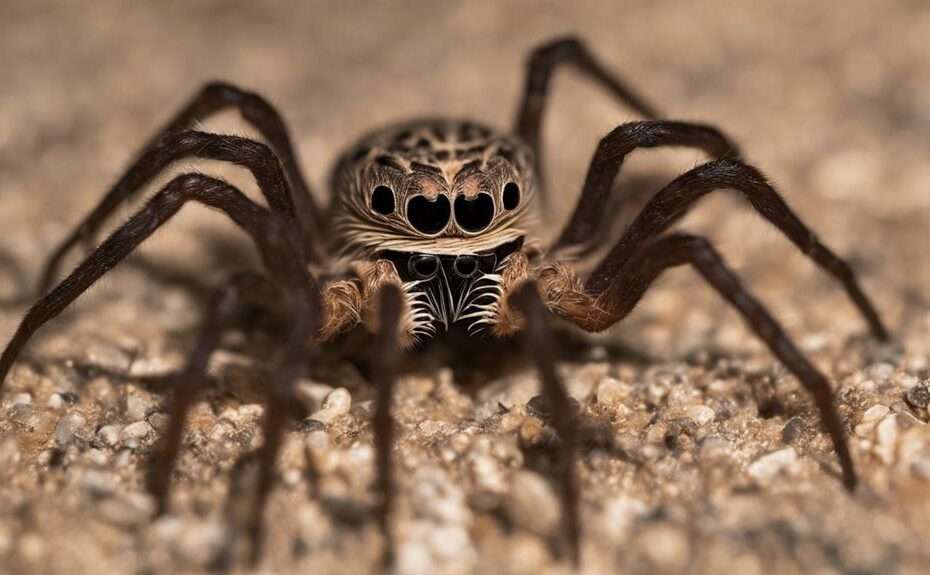
In their arid habitats, uncommon sun spider species demonstrate nocturnal behavior to evade the scorching daytime heat. These nocturnal creatures are well-adapted to the challenges of desert environments, where sunlight can be intense and temperatures soar. Seeking shelter during the day, they wait patiently for the cover of darkness to emerge. Their preference for rugged terrains with limited sunlight showcases their ability to thrive in semi-desert regions, where they can avoid the harsh conditions of the day.
The choice to be active at night allows these sun spiders to avoid predators more effectively and conserve energy during the hot daytime hours. By adapting to a nocturnal lifestyle, they maximize their hunting efficiency, preying on unsuspecting insects under the veil of darkness. Their environmental adaptation includes burrowing behavior, which serves as both protection and a place for reproduction, highlighting their resilience in harsh desert conditions. The nocturnal habits of these sun spiders reveal a strategic approach to survival in their challenging habitat.
Nocturnal Activity Patterns and Hunting Behavior
As night falls, sun spiders unleash their prowess in the art of nocturnal hunting. Their sensitive touch and keen vision guide them through the darkness, detecting even the slightest movements of unsuspecting prey.
With lightning-fast speed and precision, they navigate the shadows, effortlessly capturing insects and scorpions under the veil of night.
Nighttime Hunting Techniques
During their nighttime hunts, uncommon sun spiders, known as solifugids, employ a combination of stealthy movements and rapid bursts of speed to capture prey under the cover of darkness.
Solifugids, being nocturnal creatures, take advantage of the night to hunt for their prey items which include insects, spiders, and small animals. Their agility and speed make them skilled hunters in the dark, utilizing their keen sense of touch and vibration detection to locate potential meals efficiently.
Seeking cooler temperatures and shadows, solifugids conserve energy while on the prowl, using ambush strategies to secure their next meal. Their nocturnal activity patterns reveal a strategic approach to hunting, where they rely on their large jaws to swiftly capture unsuspecting prey under the veil of night.
Prey Detection Methods
Stealthily prowling the desert under the cloak of night, uncommon sun spiders, also known as solifugids, employ intricate prey detection methods driven by their exceptional sense of touch and vibration detection.
- Sensitive Front Appendages: Sun spiders use their specialized front appendages to detect subtle vibrations in the sand, allowing them to pinpoint the location of potential prey.
- Chemoreception: These arachnids rely on chemoreception to sense chemical cues released by nearby insects, aiding in prey detection even in complete darkness.
- Stealthy Approach: Sun spiders move silently across the desert floor, minimizing disturbances that could alert their prey, showcasing their adept prey detection strategies.
- Quick Pursuit: Once prey is detected, sun spiders swiftly pursue and capture their target, showcasing their efficient nocturnal hunting behavior.
Movement in Darkness
Under the veil of darkness, solifugids, known for their nocturnal tendencies, exhibit a strategic and calculated approach to movement in pursuit of prey. These creatures navigate the night with precision, utilizing their keen senses to detect prey such as insects, scorpions, and lizards.
During the day, solifugids seek shade, moving towards shadows to avoid the harsh sunlight, often hiding in burrows or under rocks. However, as night falls, they're drawn to light sources, using them for navigation and hunting strategies. Solifugids are commonly found in dark, quiet places like cupboards and attics, where they actively hunt for prey under the cover of darkness.
Their nocturnal habits reveal a fascinating adaptation to the rhythms of the night.
Reproduction and Unique Mating Rituals
You notice the intricate mating dance patterns of sun spiders, where males delicately stroke females with their pedipalps to induce torpor, ensuring successful reproduction.
Observing the courtship behaviors closely, you witness the males' long journeys in search of suitable mates, highlighting the importance of reproductive success rates in sustaining their populations.
These unique mating rituals not only secure genetic diversity within sun spider species but also provide a fascinating insight into their reproductive strategies.
Mating Dance Patterns
Observing the nocturnal behaviors of uncommon sun spiders reveals a fascinating mating ritual characterized by intricate dance patterns using their pedipalps to induce torpor in females. These dance patterns are crucial for initiating the mating process and ensuring reproductive success.
Here are some key points about the mating dance patterns of sun spiders:
- Solifugids engage in a unique mating ritual where males stroke females with their pedipalps in a specific pattern.
- The male's movements are designed to attract and induce torpor in females.
- Males travel long distances to find mates and perform these intricate dances to initiate mating.
- The mating dance and ritualistic behavior are essential for successful reproduction in sun spiders.
Reproductive Success Rates
Solifugids exhibit remarkable reproductive success rates attributed to their unique mating rituals and behaviors. Reproducing once a year, females lay between 50-200 eggs in a burrow, ensuring a significant number of offspring.
Males of certain species display distinctive mating behaviors, traveling long distances to find mates. Their method of inducing torpor in females by stroking them with their pedipalps before mating showcases intricate mating rituals.
After hatching, the offspring initially cluster together, providing them with a better chance of survival. However, as they progress through the nymphal stages, they disperse to explore their surroundings. This clustering behavior early on, followed by dispersal, contributes to the reproductive success rates of solifugids by increasing the chances of survival for their offspring.
Courtship Behavior Observations
The intricate courtship behavior of uncommon sun spiders involves males traveling significant distances to locate mates and utilizing their pedipalps to induce a state of torpor in females during mating. This unique mating ritual is crucial for reproductive success and species continuation. Observations reveal fascinating insights into their courtship behavior:
- Solifugids engage in a distinctive courtship behavior, with males embarking on long journeys to find potential mates.
- Males stroke females with their pedipalps, triggering a state of torpor essential for successful mating.
- Reproduction happens once annually, with females depositing 50-200 eggs within a burrow.
- Offspring initially congregate together but disperse during the nymphal stages, ensuring genetic diversity and survival.
Predatory Interactions and Feeding Habits
Hunting under the cover of darkness, sun spiders exhibit a predatory prowess that relies on their exceptional speed and agility to ambush and consume a variety of prey, ranging from insects to small vertebrates.
These nocturnal hunters engage in intense predatory interactions, actively seeking out insects, scorpions, and small vertebrates as their primary sources of food. With their powerful jaws, sun spiders crush and consume their prey, showcasing efficient feeding habits that contribute to pest control by preying on nuisance insects like cockroaches and scorpions.
Their exceptional speed and agility enable them to catch and overpower their prey swiftly during nighttime hunts, playing a crucial role in maintaining the natural balance of ecosystems. Despite their intimidating appearance, sun spiders are harmless to humans and typically only bite when provoked, utilizing their predatory skills primarily for securing food in their habitats.
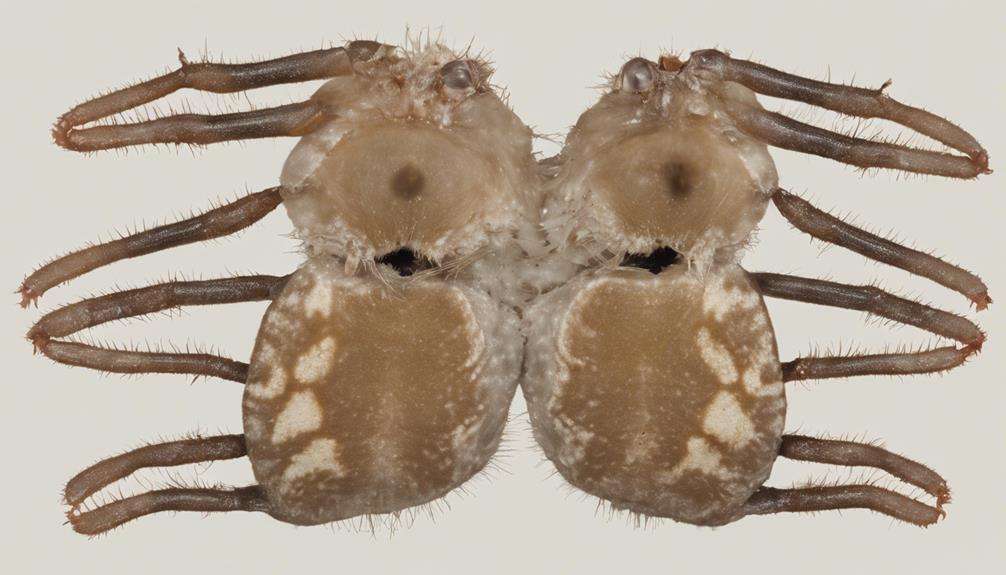
Physical Characteristics and Sensory Adaptations
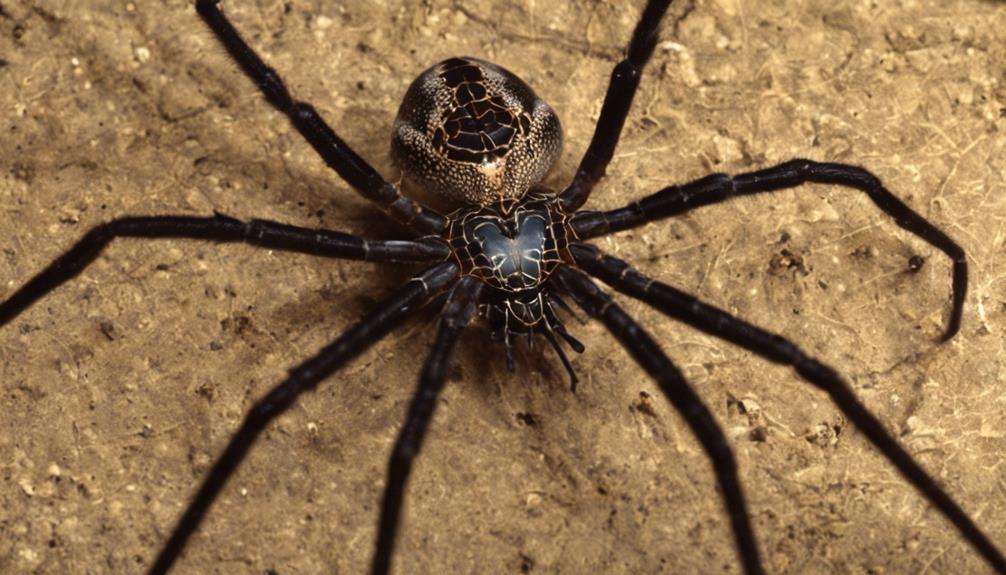

Uniquely adorned with hairy bodies and equipped with oversized jaws for efficient hunting, uncommon sun spider species display distinctive physical characteristics that enhance their predatory prowess. These features, combined with specialized sensory adaptations, contribute to their success as nocturnal hunters in desert environments.
- Nocturnal Lifestyle: Sun spiders are active during the night, allowing them to avoid extreme daytime heat and predators while maximizing their hunting efficiency in cooler temperatures.
- Oversized Jaws: Their large jaws are designed for capturing and subduing prey swiftly, giving them an advantage in securing food in their habitat.
- Sensitive Hairs: Sun spiders possess sensitive hairs on their bodies that help them detect vibrations in the environment, aiding in prey detection and navigation.
- Enhanced Vision: These creatures rely on keen eyesight and vibration-sensing organs to locate and capture prey effectively in the darkness of the night.
These physical traits and sensory adaptations collectively make uncommon sun spiders well-suited for their nocturnal hunting lifestyle, showcasing their remarkable ability to thrive in challenging desert conditions.
Conservation Status and Population Trends
Displaying a complex interplay of environmental factors and human activities, the conservation status and population trends of sun spiders demand careful scrutiny and proactive intervention for their long-term survival.
While some sun spider species are currently classified as least concern due to their widespread distribution and stable populations, others face imminent threats from habitat destruction, urbanization, and pesticide use, resulting in population declines in specific regions.
Assessing population trends for sun spiders proves challenging due to limited research and data availability on their abundance and distribution across various habitats. Conservation efforts aimed at safeguarding sun spiders involve habitat preservation, reducing pesticide usage, and increasing awareness about their crucial role in pest control within ecosystems.
Monitoring population dynamics and conducting further research on sun spider species are essential steps in formulating effective conservation strategies to ensure their sustained existence in the face of evolving environmental pressures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Sun Spiders Nocturnal?
Yes, sun spiders are nocturnal creatures. They exhibit photonegative behavior, moving towards darkness during the day. At night, they hunt efficiently under cover of darkness, utilizing their nocturnal hunting techniques. They hide in daytime spots to avoid extreme temperatures.
What Is the Behavior of a Sun Spider?
You observe a sun spider's behavior closely. At night, they engage in nocturnal hunting, moving swiftly towards light. During the day, they retreat to burrows, displaying territorial behavior. Their habits reveal efficient and strategic predators.
Why Do Some Spiders Only Come Out at Night?
Spiders come out at night due to their circadian rhythms, which give them predatory advantages. Environmental factors like temperature and predator avoidance influence nocturnal behavior. Hunting when prey is active and using low light vision are key strategies.
What Are the Unique Characteristics of Solifugae?
Solifugae boast unique characteristics in anatomy, hunting techniques, and burrowing habits. Their powerful jaws, efficient tracheal system, and lack of silk-producing organs set them apart. They rely on jaws for prey, excel in oxygen intake, and burrow for shelter.
Conclusion
As you reflect on the nocturnal behavior of uncommon sun spider species, you can't help but marvel at their mysterious ways. These creatures, with their stealthy hunting habits and unique adaptations, are truly nature's enigmatic marvels.
Their presence in the desert-like environments is like a shimmering gem in the vast expanse of the night, a testament to the intricate beauty of the natural world.
So take a moment to appreciate these fascinating arachnids, for they're truly a wonder to behold.